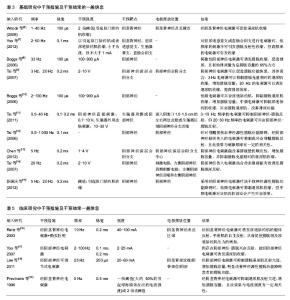
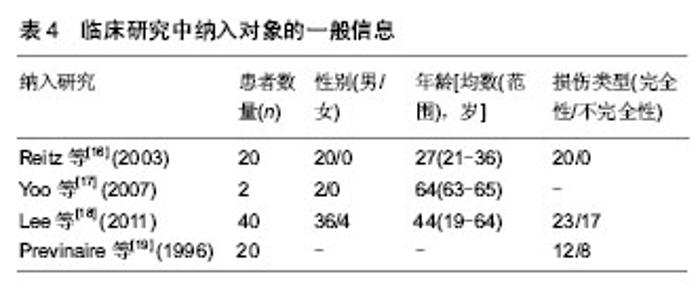
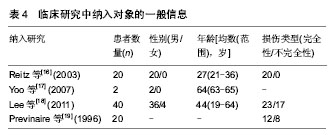
| [1] 廖利民,吴娟,鞠彦合.脊髓损伤患者泌尿系管理与临床康复指南[J].中国康复理论与实践,2013,19(4):301-317.
[2] Frankel HL,Coll JR,Charlifue SW,et a1.Long-term survival in spinal cord injury: a fifty year investigation.Spinal Cord. 1998; 36(4):266-274.
[3] 刘铁军,赵盟杰,沙可夫.相对安全膀胱容量间歇导尿法保护上尿路的临床研究[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2010,16(8): 792-793.
[4] 杨杰.口服托特罗定联合膀胱内注射肉毒素治疗OAB临床观察[J].山东医药,2013,53(27):83-84.
[5] Dalmose AL,Rijkhoff NJ,Kirkeby HJ,et al. Conditional stimulation of the dorsal penile/clitoral nerve may increase cystometric capacity in patients with spinal cord injury. Neurourol Urodyn.2003;22(2):130-137.
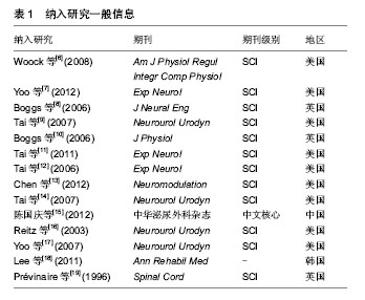
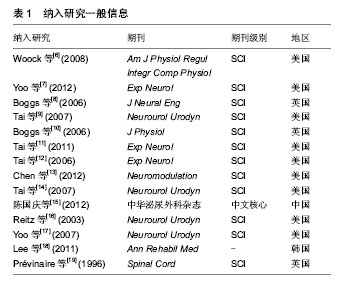
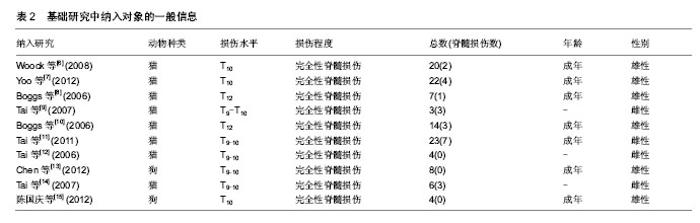
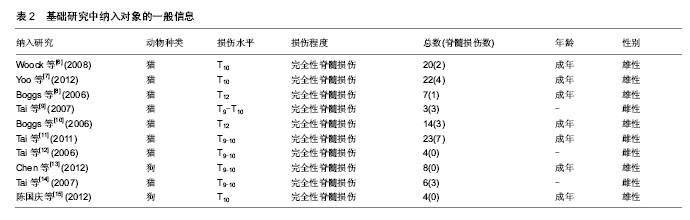
[6] Woock JP,Yoo PB,Grill WM.Activation and inhibition of the micturition reflex by penile afferents in the cat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.2008;294 (6):1880-1889.
[7] Yoo PB, Woock JP, Grill WM.Bladder activation by selective stimulation of pudendal nerve afferents in the cat. Experimental Neurology.2008;212(1):218-225.
[8] Boggs JW, Wenzel BJ, Gustafson KJ.Bladder emptying by intermittent electrical stimulation of the pudendal nerve.J Neural Eng.2006;3 (1): 43-51.
[9] Tai C,Wang JC , Wang XC,et al. Bladder Inhibition or Voiding Induced by Pudendal Nerve Stimulation in Chronic Spinal Cord Injured Cats.Neurourol Urodyn.2007;26(4):570-577.
[10] Boggs JW, Wenzel BJ, Gustafson KJ, et al. Frequency- dependent selection of reflexes by pudendal afferents in the cat.J Physiol.2006;577(1):115-126.
[11] Tai C, Chen M , Shen B,et al.Plasticity of urinary bladder reflexes evoked by stimulation of pudendal afferent nerves after chronic spinal cord injury in cats.Exp Neurol.2011;228 (1):109-117.
[12] Tai C,Smerin SE,de Groat WC,et al.Pudendal-to-bladder reflex in chronic spinal-cord-injured cats. Exp Neurol. 2006;197(1): 225-234.
[13] Chen G, Liao L, Dong Q,et al.The Inhibitory Effects of Pudendal Nerve Stimulation on Bladder Overactivity in Spinal Cord Injury Dogs: Is Early Stimulation Necessary? Neuromodulation.2012;15(3): 232-237.
[14] Tai C,Wang J,Wang X,et al.Voiding Reflex in Chronic Spinal Cord Injured Cats Induced by Stimulating and Blocking Pudendal Nerves. Neurourol Urodyn.2007;26 (6): 879-886.
[15] 陈国庆,廖利民,董谦,等.不同频率的阴部神经电刺激对骶上脊髓损伤犬神经源性膀胱功能障碍的影响[J].中华泌尿外科, 2012, 33(9):678-681.
[16] Reitz A,Schmid DM,Curt A,et al.Afferent Fibers of the Pudendal Nerve Modulate Sympathetic Neurons Controlling the Bladder Neck. Neurourol Urodyn.2003;22 (6): 597-601.
[17] Yoo PB, Klein SM, Grafstein NH,et al.Pudendal Nerve Stimulation Evokes Reflex Bladder Contractions in Persons With Chronic Spinal Cord Injury.Neurourol Urodyn.2007;26(7): 1020-1023.
[18] Lee YH, Jung Moon Kim, Hyung Tae Im,.Semiconditional Electrical Stimulation of Pudendal Nerve Afferents Stimulation to Manage Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Ann Rehabil Med.2011;35:605-612.
[19] Prévinaire JG, Soler JM, Perrigot M,et al.Short-term effect of pudendal nerve electrical stimulation on detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injury patients: importance of current strength. Paraplegia.1996;34(2): 95-99.
[20] 廖利民,鞠彦合.第三届国际尿失禁咨询委员会最终推荐意见:神经源性尿失禁部分[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2005,11(11): 881-882.
[21] 李凝.脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱尿潴留的针刺康复疗效观察[D]南京:南京中医药大学,2011:1-33.
[22] Martin Braun P, Araneibia Fernandez MI, Martinez Portillo FJ, et al. Continuous bilateral sacral neuromodulation as a minimally invasive implantation technique in patients with functional bladder changes. Arch ESP Urol.2003; 56(5): 497-450.
[23] Yokozuka M,Namima T,Nakagawa H,et al.Effects and Indications of Sacral Surface Therapeutic Electrical Stimulation in Refractory Urinary Incontinence.Clin Rehabil. 2004;18(8): 899-907.
[24] Schumacher S, Bross S, Scheepe JR, et al.Extradural cold block for selective neurostimulation of the bladder: development of a new technique.J Urol. 1999;161(3): 950-954.
[25] Bosch JL, Groen J. Sacral nerve neuromodulation in the treatment of patients with refractory motor urge inconti-nence: long-term results of a prospective longitudinal study. J Urol. 2000;163(4):1219 -1222.
[26] 孙鸿斌,尹维田,孙玉霞.阴部神经的临床应用解剖[J].2004,30(2): 242-243.
[27] Hansen J,Media S, Nøhr M,et al.Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injuried patients by condition electrical stimulation.J Urol.2005;173:2035-2039. |